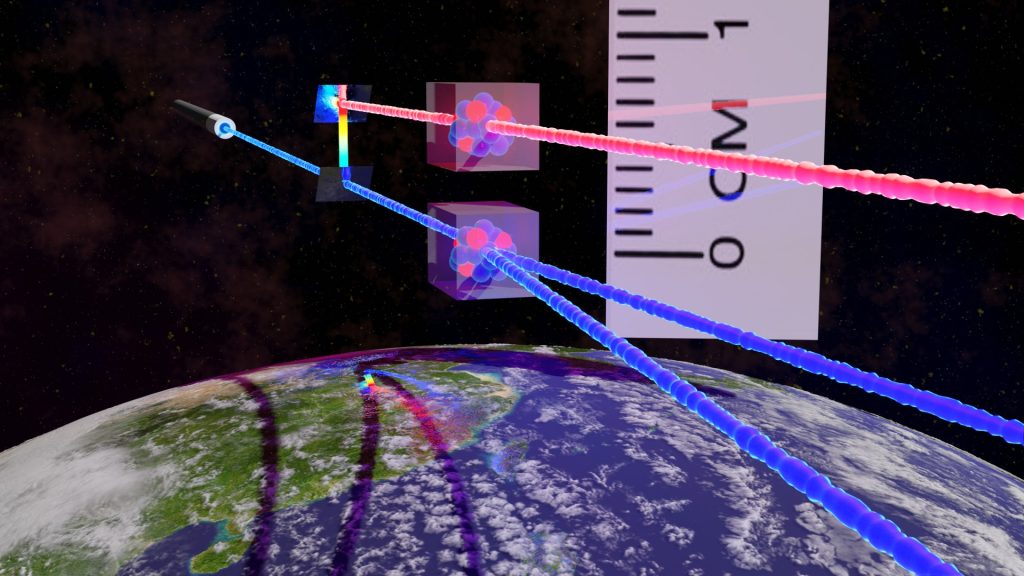
Figure. Sensing the difference of gravity in 1mm altitude change on Earth using an SXWG and 45Sc nuclear clock transition.
Phys. Rev. Research 7, 013158
Shin-Yu Lee, Sven Ahrens, and Wen-Te Liao
Gravitationally sensitive structured x-ray optics using nuclear resonances
我們與上海師範大學的Sven Ahrens教授合作設計一種新型結構化X光波導管[structured X-ray waveguide (SXWG)],能探測地球上1毫米高度變化所引起的重力差異。根據X光通過波導管傳播行為與量子粒子行為之間的類比,我們在光學薛丁格方程式的引導下設計了SXWG,將鈧-45-碳交錯的週期性結構夾在兩個鉑包覆層之間。其中鈧-45同位素的極窄原子核鐘躍遷,其自然線寬約為2 Hz,躍遷能量約為12.4 keV。如此窄的線寬能用來檢測到鈧-45與共振X光之間在1毫米高度變化下的微小交互作用差異。因此改變SXWG的高度將因重力紅位移效應而改變兩個X光波導管模態之間的耦合強度。我們的計算結果顯示,SXWG的X光輸出光班分佈會受到高度變化的影響。故透過檢視光班的變化便能得知SXWG與X光光源之間的高度差。而使用其他同位素,如釷-229、銀-109等,甚至可以達到微米等級的靈敏度。
We collaborate with Prof. Sven Ahrens from Shanghai Normal University to design a novel structured X-ray waveguide (SXWG) capable of detecting gravitational differences caused by height changes as small as 1 millimeter on Earth. Based on an analogy between the propagation of X-rays through a waveguide and the behavior of quantum particles, we designed the SXWG under the guidance of the optical Schrödinger equation, sandwiching a periodic structure of 45Sc scandium-carbon interleaved layers between two platinum-coated layers. The scandium isotope has an extremely narrow nuclear clock transition, with a natural linewidth of about 2 Hz and a transition energy of approximately 12.4 keV. Such a narrow linewidth can be used to detect tiny interaction differences between 45Sc and resonant X-rays under a 1-millimeter height change. Thus, altering the height of the SXWG will change the coupling strength between two X-ray waveguide modes due to the gravitational redshift effect. Our calculations show that the X-ray output intensity distribution of the SXWG is affected by height changes. Therefore, by examining the changes in the light pattern, the height difference between the SXWG and the X-ray source can be determined. Using other isotopes, such as 229Th or 109Ag, can even achieve sensitivity at the micrometer level.

Figure. Sensing the difference of gravity in 1mm altitude change on Earth using an SXWG and 45Sc nuclear clock transition.